2022 Compensation Survey
In May 2022, EPA conducted an anonymous survey on salaries and benefits of its members, commissioned by the EPA Board of Directors and conducted by 5by5, an independent research firm based in Nashville.
This is the third time EPA has conducted this survey with prior surveys in 2016 and 2019. The survey was a followup to the 2019 survey to see what has changed.
The survey was promoted through a postcard mailing to 562 individuals and four emails sent to 556 of the same individuals for whom we had email addresses. The contact list was made up of staff names from current EPA member publications, numbering more than 200. EPA does not know how many total workers are employed by all publications.
There were 114 responses to the survey, 20% of the targeted group. EPA does not know how many publications or which publications are represented in the survey.
The charts and statistics in this post reflect the key findings from the survey. For the downloadable report, click here.
For the 2019 survey results, click here.
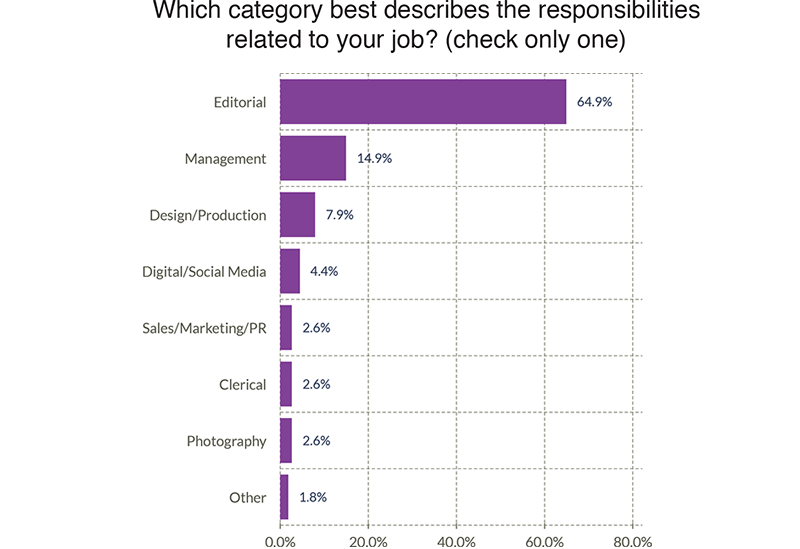
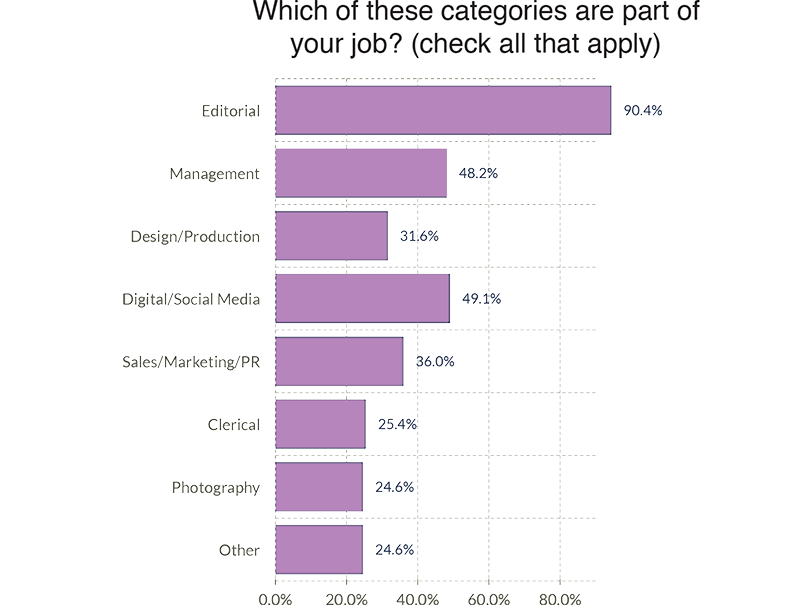
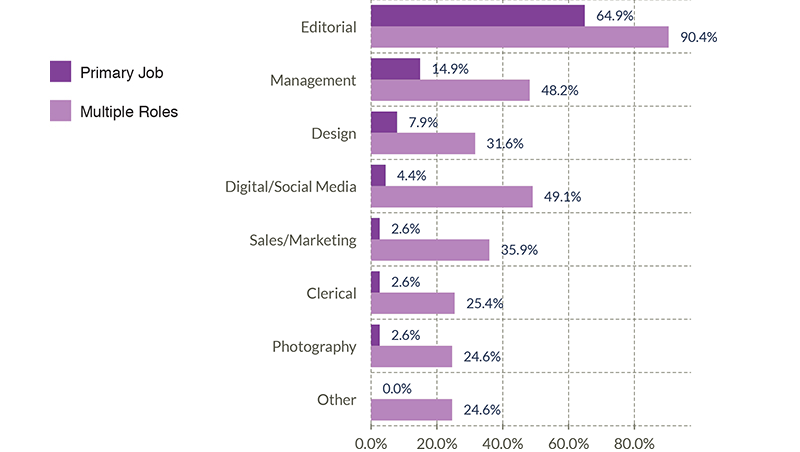
The next graph combines both charts from above. The light purple bar illustrates the percentage of all workers who perform some of these responsibilities, whether or not it is their primary job. For example, while only 4.4% of jobs are primarily Digital/Social Media (dark purple bar), 49.1% of jobs have at least some responsibilities in Digital/Social Media (light purple bar).
Salary Range
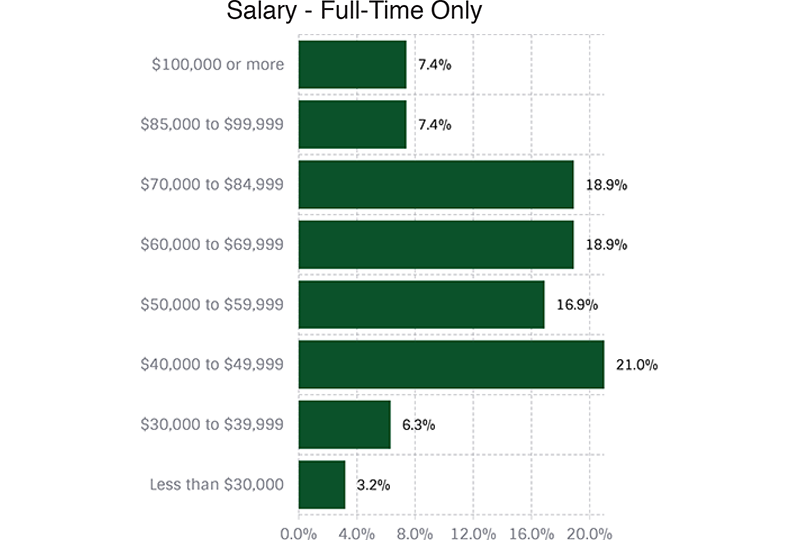
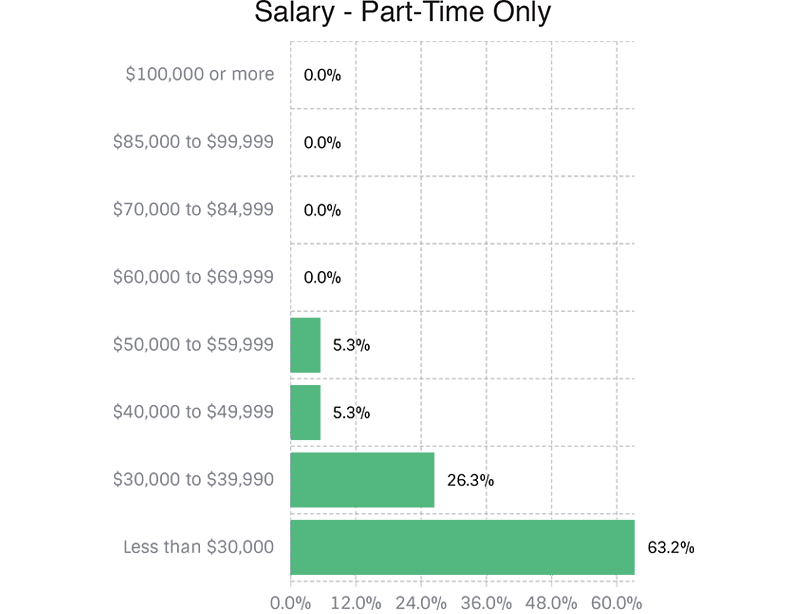
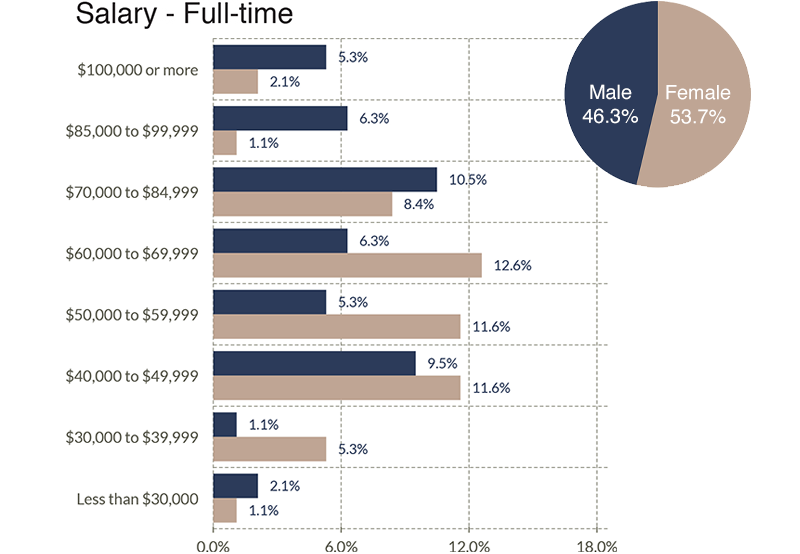
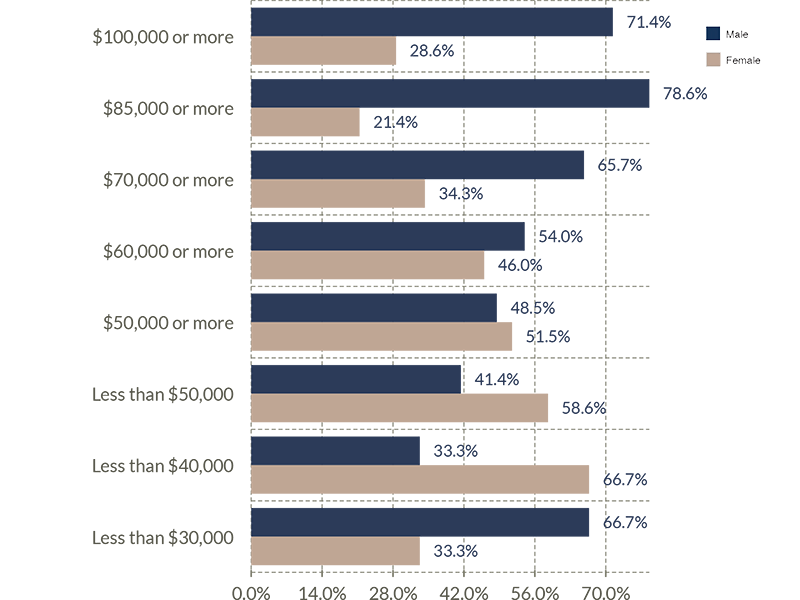
Salary Range by Gender
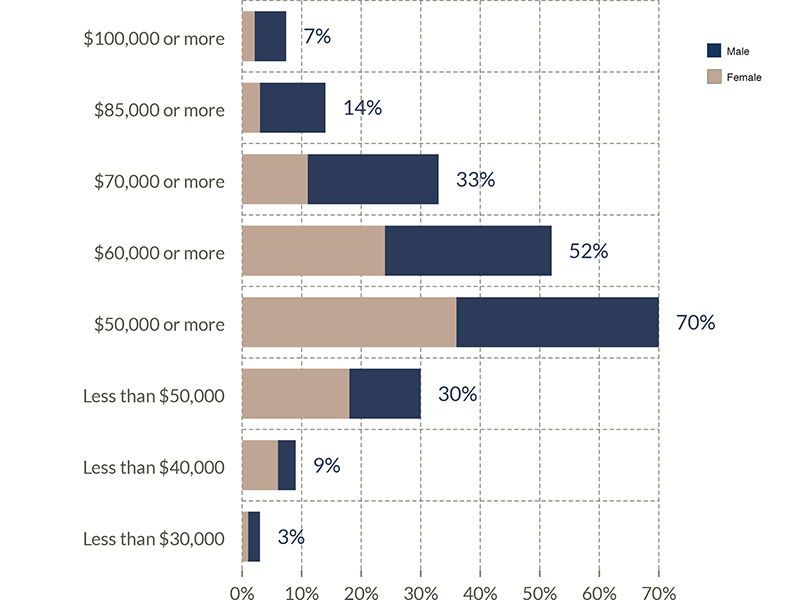
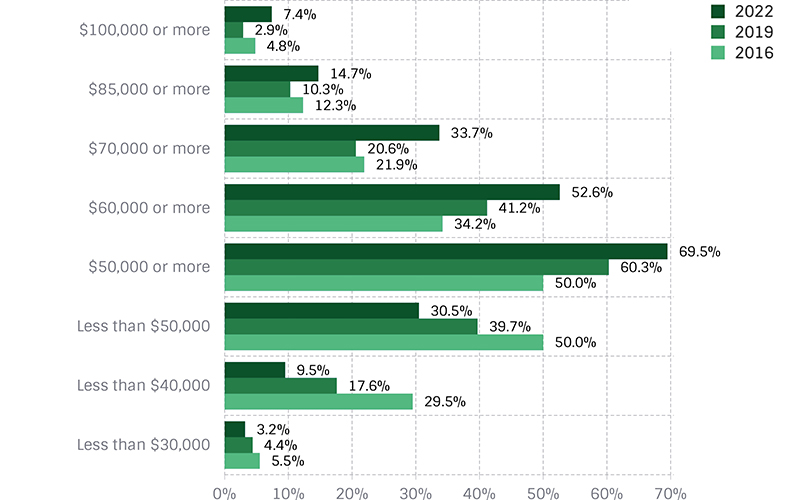
• 7.4% of all full-time workers earn $100,000 or higher
* 71.4% are male | 28.6% are female
• 14.7% of all full-time workers earn $85,000 or higher
* 78.5% are male | 21.5% are female
• 33.7% of all full-time workers earn $70,000 or higher
* 65.6% are male | 34.4% are female
• 52.6% of all full-time workers earn $60,000 or higher
* 54.0% are male | 46.0% are female
• 69.5% of all full-time workers earn $50,000 or higher
* 48.5% are male | 51.5% are female
• 30.5% of all full-time workers earn less than $50,000
* 41.4% are male | 58.6% are female
• 9.5% of all full-time workers earn less than $40,000
* 33.3% are male | 66.7% are female
• 3.2% of all full-time workers earn less than $30,000
* 66.7% are male | 33.3% are female
• 61.4% of all full-time male workers earn $60,000 or higher
• 45.1% of all full-time female workers earn $60,000 or higher
The following chart shows the aggregate salary ranges for both female and male with combined levels equal to 100%.
The next three graphs illustrate salary ranges broken out by the three primary categories of full-time workers.
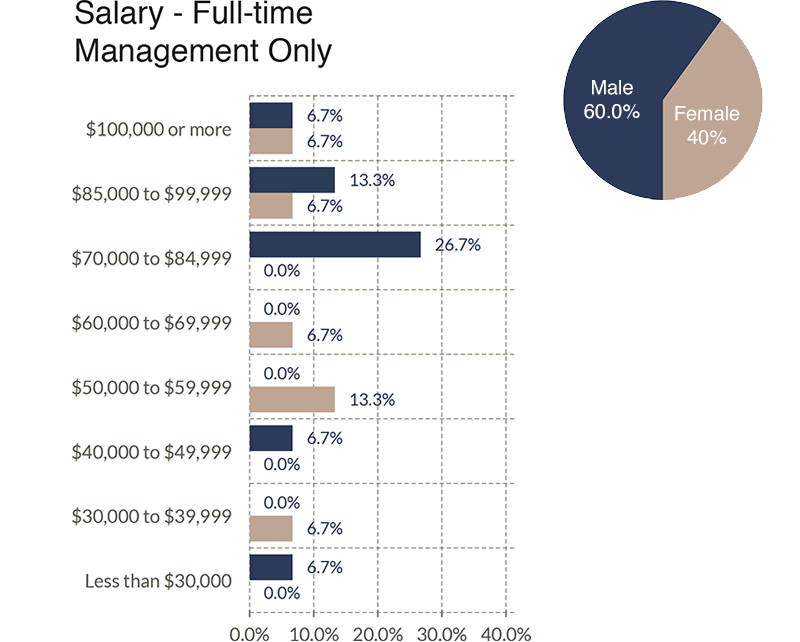
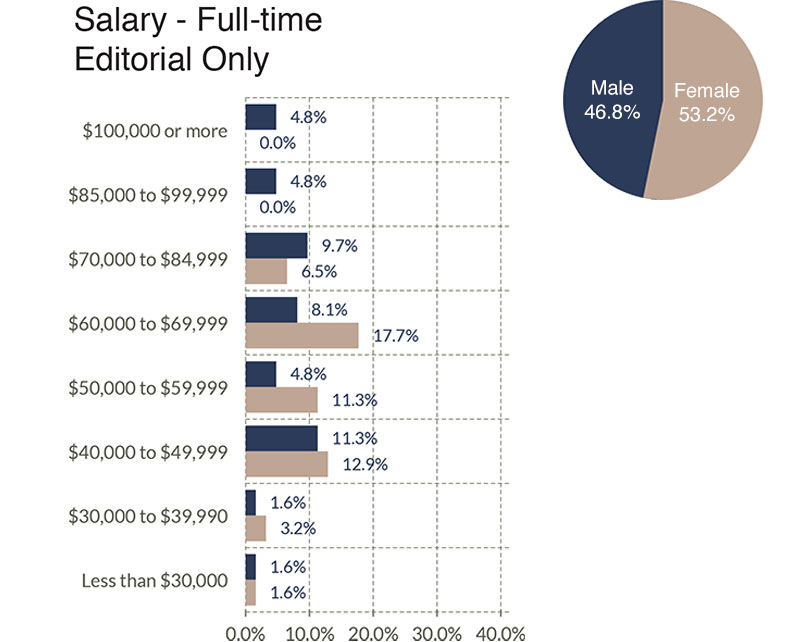
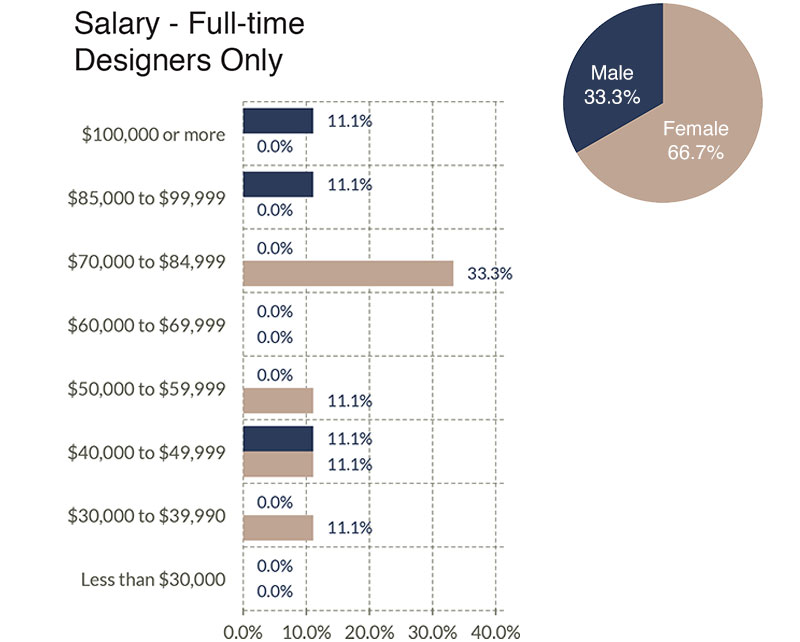
Benefits Offered
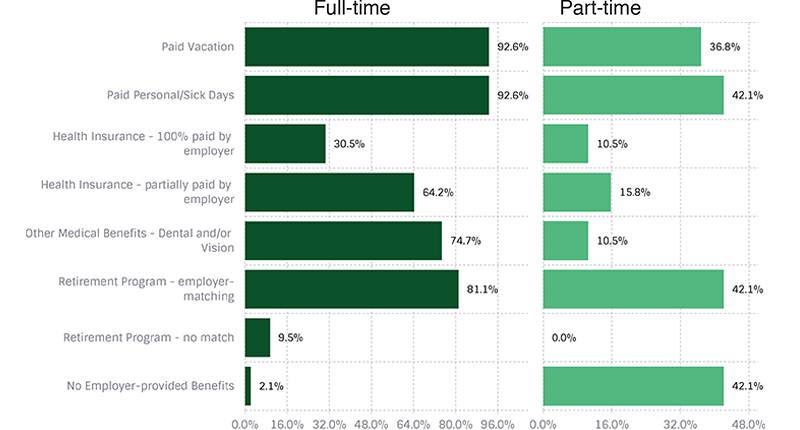
Other benefits mentioned include disability insurance, life insurance and tuition assistance.
Comparing Salary Ranges
This compares salary ranges and the percentage of those paid within those ranges — from our triennial surveys in 2016, 2019 and 2022. The first graph (green) includes all full-time salaries. The tan graph represents female salaries and the blue graph represents male salaries.
All Full-Time Salaries
All Female Full-Time Salaries
![]()
All Male Full-Time Salaries
![]()
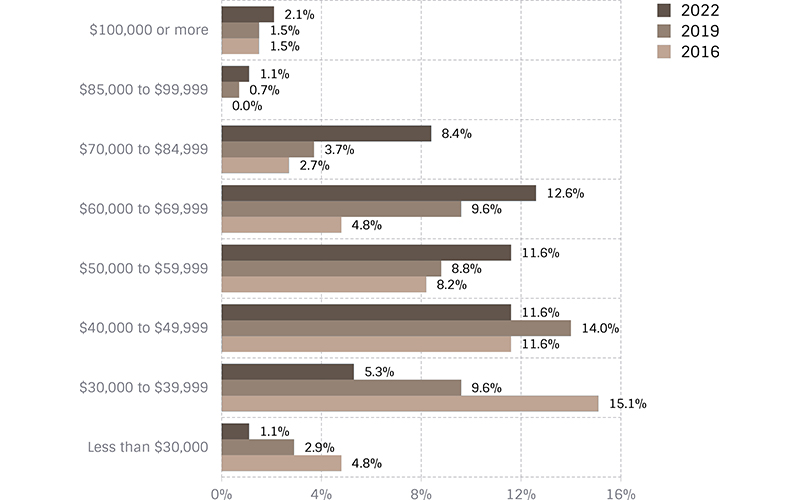
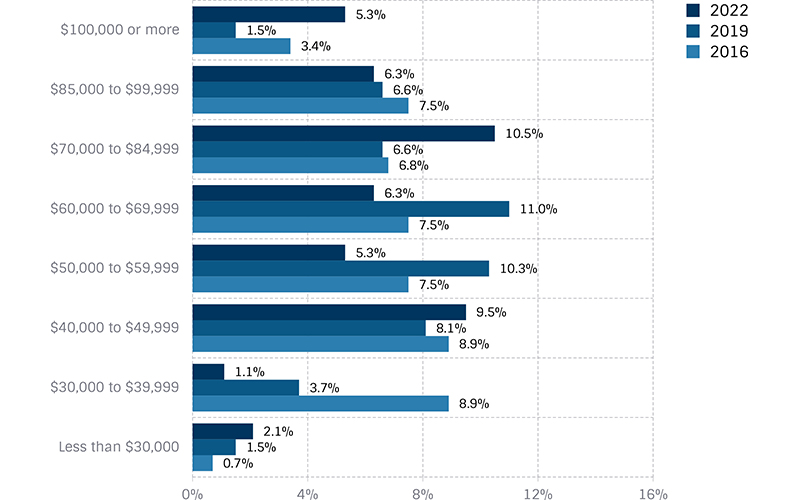
Comparing Salary Levels
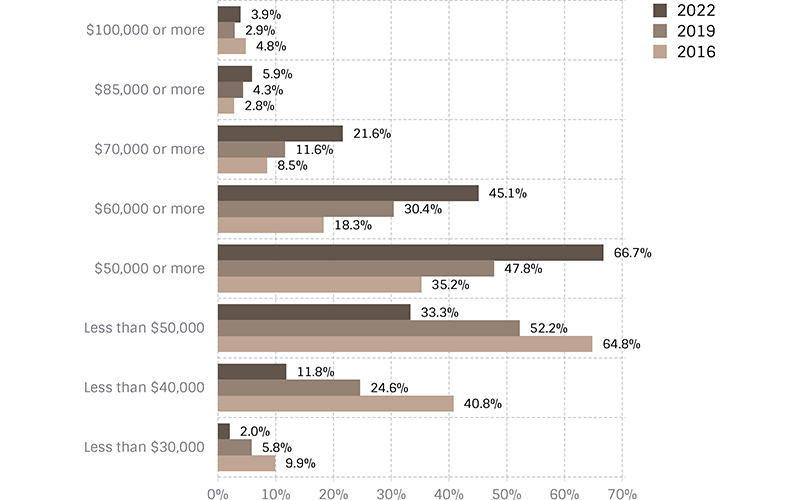
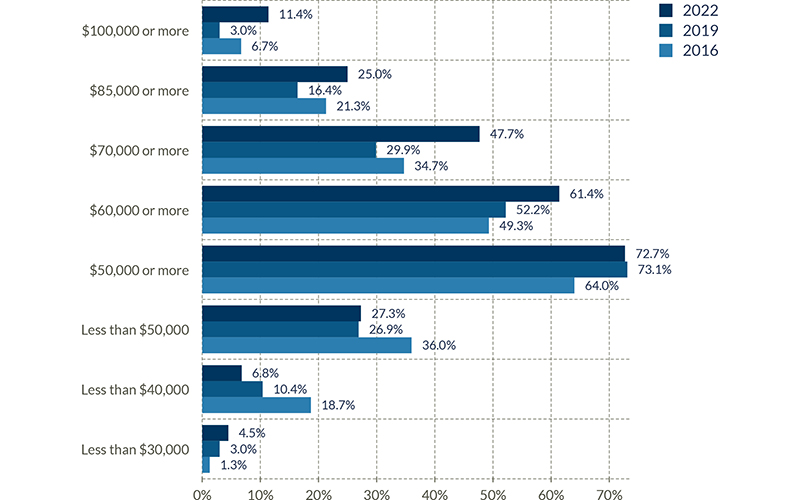
This compares the percentage of those paid above or below varying levels — from our triennial surveys in 2016, 2019 and 2022. The first graph (green) includes all full-time salaries. The tan graph represents female salaries and the blue graph represents male salaries.
All Full-time Salaries

All Female Full-time Salaries
All Male Full-time Salaries
2019 vs 2022 Compensation Survey Comparison
Significant Points of Change
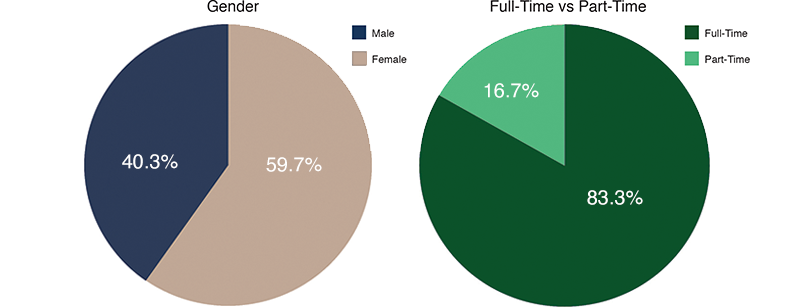
- Female vs. male gender majority increased from 55.8% to 59.7% when considering both full-time and part-time roles
- Female vs. male gender majority increased from 50.8% to 53.7% when considering only full-time roles
- Full-time vs. part-time status decreased from 88.3% to 83.3%
- Those whose roles include editorial responsibilities increased from 78.6% to 90.4%
- Those whose roles included clerical duties increased from 16.9% to 25.4%
- Those whose roles include digital/social media responsibilities decreased from 54.5% to 49.1%
- 23% fewer people have design roles as part of their responsibilities
- 33% earn $70,000 or more (compared to 20% in 2019)
- 52% earn $60,000 or more (compared to 41% in 2019)
- 70% earn $50,000 or more (compared to 60% in 2019)
- 30% earn less than $50,000 (compared to 40% in 2019)
- The primary full-time salary range increased from $40,000 – $70,000 to $50,000 to $85,000
- The percentage of males earning $60,000 or more increased from 52.2% to 61.4%
- The percentage of females earning $60,000 or more increased from 30.4% to 45.1%
• The ratio of female to male salaries increased in the higher tiers
———* $60,000 or more: From 37.5% to 46.0%
———* $70,000 or more: From 28.6% to 34.4%
———* $85,000 or more: 21.4% (unchanged)
• The ratio of females to males in management decreased from 54.5% to 40%
Posted July 28, 2022



